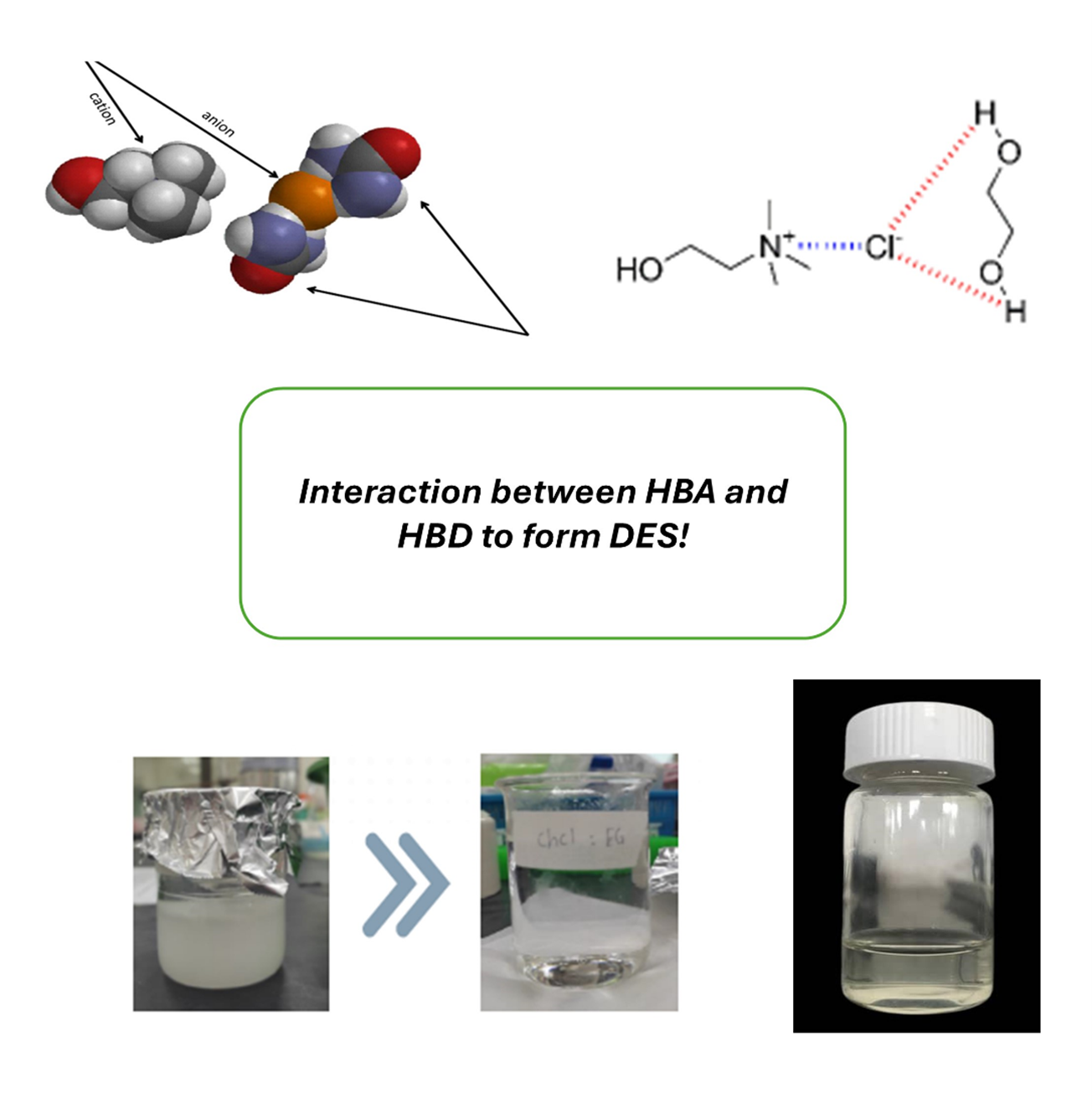
Deep eutectic solvents (DES) are a class of green solvents formed by any combination of a hydrogen bond donor and a hydrogen bond acceptor, creating a eutectic mixture with a lower melting point than its individual components. Finding the right ratio is crucial, as it determines whether the mixture reaches the eutectic point, where it remains stable in a liquid state. They are biodegradable, non-volatile, and highly tunable, making them an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional organic solvents.
Consider choline chloride and urea; the former is a salt, and the latter is a compound. Both exists as a solid in room temperature.
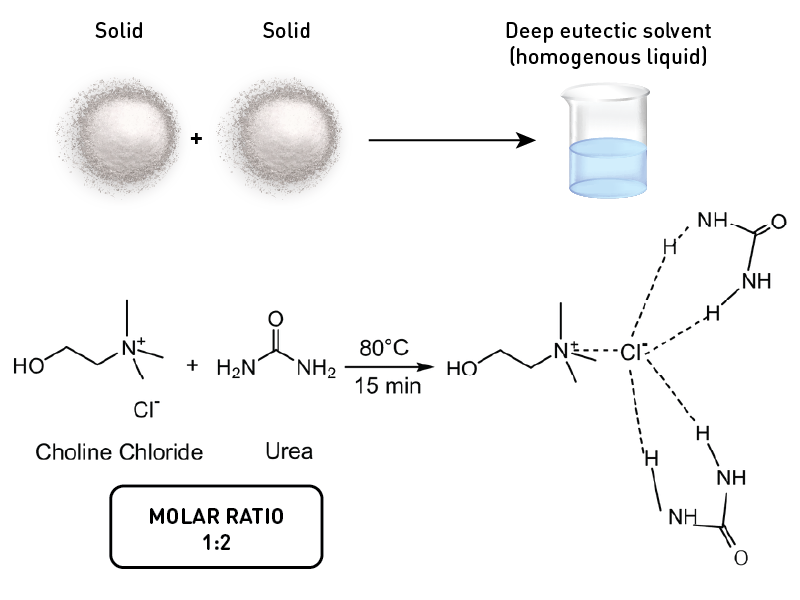
But when you mix these two, it results in a liquid! Isn’t it amazing? This magical combination of solids is what we call deep eutectic solvent, or DES for short. A DES combines two chemicals either solid-solid or liquid-solid which resulted in a liquid product. This is because the eutectic point reached by the mixture which is way below the individual melting point of the two substances.
The eutectic point refers to the lowest temperature at which a mixture remains stable at a given pressure. When the correct ratio, temperature, and pressure conditions are met, the combined solid transitions into a liquid and remains in that state indefinitely. This unique characteristic makes eutectic systems particularly interesting in various scientific and industrial applications.
Above is the example of a phase diagram of a DES where the eutectic point was calculated by extrapolations. In order to get a liquid mixture, the temperature has to be kept at least on the eutectic point. Some DES reached its eutectic point at room temperature whereas some requires a higher temperature to reach its eutectic point. However not all solid mixtures can have eutectic points. That will be a discussion for another !
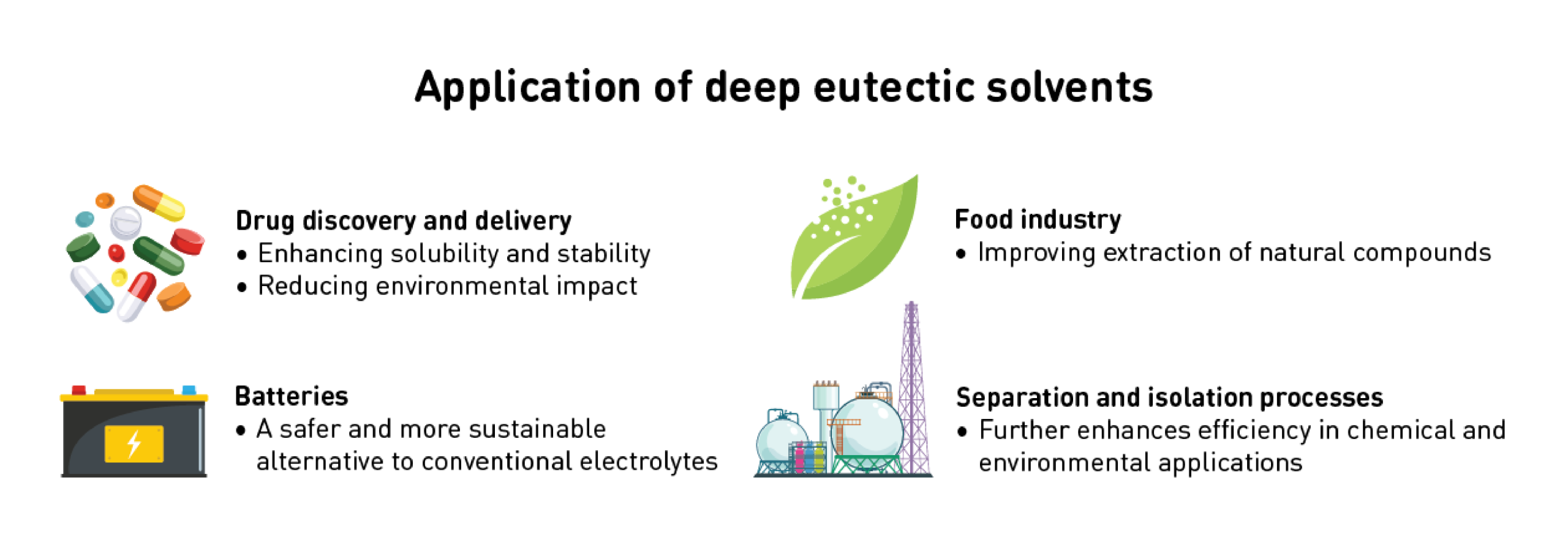
DES offer more than just laboratory appeal—they have significant real-world applications. From the chemical and biotechnology industries to innovative solvent systems, these green alternatives are transforming various fields.
DES play a crucial role in drug discovery and delivery by enhancing solubility and stability while reducing environmental impact. They also contribute to the food industry and improve the extraction of natural compounds. Additionally, DES are gaining attention as electrolytes in batteries, providing a safer and more sustainable alternative to conventional electrolytes. Their use in separation and isolation processes further enhances efficiency in chemical and environmental applications, making them valuable across multiple sectors.
However, DES are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Their high viscosity, broad polarity range, and compatibility with certain compounds can present challenges in some applications. Nevertheless, their tunability allows for adjustments in composition to better suit our specific needs.