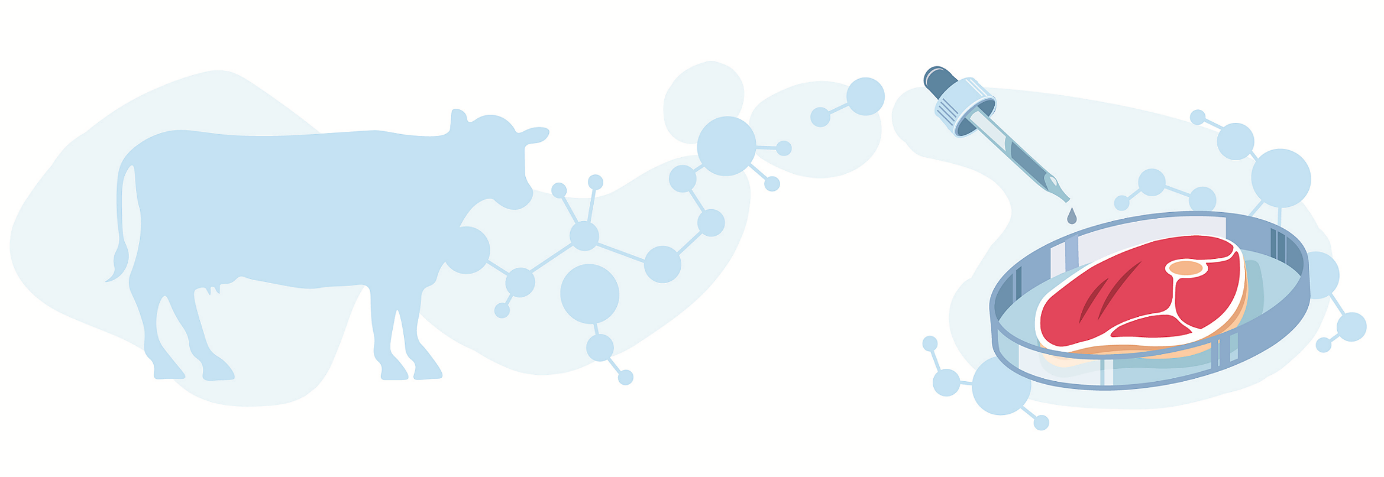
Humankind has been consuming meat since the Stone Age, and our ancestors ate any animal they could get their hands on. However, science has found a way to produce meat without killing a single animal. How? Through lab-grown meat. This new “meat” production option has been constantly receiving public attention.
What is lab-grown meat? As the name suggests, the meat is grown in a laboratory rather than from raising and slaughtering livestock. Is lab-grown meat any different from traditional meat? Both are biologically similar. However, the source of these meats is different as lab-grown meat is harvested in the lab, whereas traditional meats are from animals raised and slaughtered, particularly for meat.
Lab-grown meat is only possible with stem cells, the building blocks of muscles and other organs for the specific animal of interest. Consider an example of lab-grown meat from cows; researchers will start creating cultured meat from cow’s stem cells by placing it in Petri dishes with all the necessary nutrients to grow the muscle cells. When sufficient muscle fibres have grown, we will get a lab-grown beef.
Lab-grown meat aims to reduce or replace conventional ways of producing animal meat. The production of conventional meat causes many negative effects on humans and the environment, making lab-grown meat an alternative to reduce these effects. Water pollution is a common issue in the livestock industry as animals’ waste is washed into the nearby water source. Water pollution will not only affect animals but also humans that are dependent on the water source for drinking. The contaminated water can cause various health issues, including headaches, runny noses, and diarrhea in humans. Besides, clearing lands for farming causes many trees to be cut down, contributing to the production of greenhouse gases, which are factors in climate change. This makes lab-grown meat eco-friendly as it requires 45% less energy, 99% less land, and 96% fewer greenhouse gas emissions than traditional meats.
One might wonder, what drives the demand for lab-grown meat globally? Lab-grown meat can create a more sustainable global food system as it reduces animal slaughtering and puts significant pressure on food systems, which is contributed by the negative effects of conventional meat. Lab-grown meat can also solve the food security issues related to the growing human population.
To date, Singapore is the first and only country to approve lab-grown chicken meat produced by a US-based company for the consumption of the public. Although many countries are still considering lab-grown meat, some of these countries have taken the initiative to develop policies and guidelines, which is a huge step for the lab-grown meat industry. Many claim that lab-grown meat cannot replace conventional meat as the production of lab-grown meat is expensive and produces less meat than traditional meat. The recent advancement in science proves this wrong as researchers can produce different types of lab-grown meat, such as chicken, duck and lamb, for reasonable prices, and down the road, the prices are expected to reduce to be similar or lower than the price of conventional meat.
Researchers can control the nutritional content of lab-grown meat during its production. Growing meat in labs allows researchers to add the necessary nutrients and control the fat content, allowing lab-grown meat to be nutritious and a healthier substitute for conventional meat. This is because lab-grown meat does not contain saturated fats and growth hormones, which are commonly found in conventional meat, that cause heart diseases, diabetes, and cancers.
The lab-grown meat industry is booming because of the advancement of science, and in just a few years, we could see ourselves ordering lab-grown meat from restaurant menus and enjoying it.